
Scores on these subscales can also be combined to create two higher-order summary scores: the physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS). The SF-36 consists of 8 domains, which assess physical function (PF), role physical (RP), bodily pain (BP), global health (GH), vitality (VI), social function (SF), role emotional (RE) and mental health (MH).

The SF-36 has been extensively validated as a measure of QoL in multiple populations and is the most widely used and evaluated QoL outcome measure. QoL is more frequently measured (in 19 % of studies), most often with the Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36 ). ĭespite its prevalence and importance, mental health is rarely measured either in rheumatological research or in clinical practice, reported as an outcome in less than 8 % of published research. Common mental disorders such as pMDD or probable generalised anxiety disorder (pGAD) can have implications for long-term health outcomes depression and anxiety are associated with increased fatigue, impaired long-term disease activity and physical disability, and reduced treatment efficacy. The prevalence of depression in this condition is high, with a recent meta-analysis revealing that an estimated 38.8 % of patients screen positive for probable major depressive disorder (pMDD) according to the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9 ). Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, painful, progressive condition, which has a substantial impact on patients’ quality-of-life (QoL).
Overall, optimal use of the SF-36 for screening for mental disorder may be through using the MCS with a threshold of ≤38 to identify the presence of either depression or anxiety. This analysis may increase the utility of a widely-used questionnaire. A threshold of ≤38 could be used to detect either depression or anxiety with a sensitivity of 87.5 %, specificity of 80.3 % and accuracy of 82.8 %. A threshold of ≤40 had sensitivity and specificity of 92.3 and 70.2 % respectively to detect depression, correctly classifying 76.3 % of patients. The MCS with a threshold of ≤35 had sensitivity and specificity of 85.7 and 81.9 % respectively to detect anxiety, correctly classifying 82.8 % of patients with probable anxiety disorder. A threshold of ≤56 had sensitivity and specificity of 92.6 and 73.2 % respectively to detect depression, correctly classifying 78.6 % of patients, and the same threshold could also be used to detect either depression or anxiety with a sensitivity of 87.9 %, specificity of 76.9 % and accuracy of 80.6 %. The MH with a threshold of ≤52 had sensitivity and specificity of 81.0 and 71.4 % respectively to detect anxiety, correctly classifying 73.5 % of patients with probable anxiety disorder.

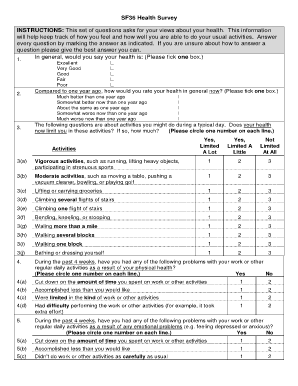
Sensitivity and specificity of the SF-36 were established using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, and area under the curve (AUC) compared the performance of the SF-36 components with the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9) for depression and the 7-item Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD7) questionnaire for anxiety. MH and MCS scores were compared against depression and anxiety data collected using validated measures as part of routine clinical practice. SF-36 data were collected in 100 hospital outpatients with rheumatoid arthritis. This study aimed to assess the accuracy of the Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) mental health subscale (MH) and mental component summary (MCS) scores in identifying the presence of probable major depressive or anxiety disorder in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
